In this article, we’ll explain what generative AI is, some current AI in healthcare examples, and what the future might hold for generative AI in healthcare.
Health and social care is a constantly evolving sector. While the primary goal is to always provide the best service possible, the approach and practices we apply, together with the tools we use, have changed over time. What was once best practice may now be deemed outdated.
Today, artificial intelligence (AI) is a tool that can help to simplify our lives as care professionals. And some organisations are already using it in their daily work practices. As generative AI becomes more commonplace and evolves, it could make significant changes to the health and social care landscape.
Let’s get started…

Table of Contents
AI in healthcare: the basics
AI is already being used in lots of areas of healthcare. Chances are, you’ve come across it, even if you don’t realise it. Here’s what you need to know:
What is AI?
AI stands for artificial intelligence. Traditional AI uses data to predict an action to take. That action might be making a prediction, giving a pre-programmed response, or activating another system.
One very common example of this is facial recognition, where AI searches through a database of images to see whether it should trigger an action.
Another area you may be familiar with is monitoring systems, where AI compares content to previous data sets to see whether it should trigger an alert. These systems may be used for everything from a continuous glucose monitor to a computer flagging up potential fraud.

What is generative AI?
Generative AI can create new content, based on patterns that it’s seen before.
You may have heard of AI models such as ChatGPT and Dall-E. ChatGPT is a chatbot that can generate text in response to a prompt, and Dall-E can create images. They’re both generative AI tools.
You can experiment with generative AI by using our handy chatbot tool below.
Please note: All AI-generated output should be vetted by an experienced care professional before any action is taken. Never input sensitive information into a chatbot.
What’s the difference between AI and generative AI?
Traditional AI will always do one of the same actions, based on the input it receives. However, generative AI generates new content, based on its knowledge base.
You may hear the two types of AI referred to as predictive or traditional AI and generative AI.
Let’s use the example of a chat facility on a care organisation’s website. A traditional AI chatbot will respond to your questions by looking for key words, such as care or dementia. It will give you a pre-programmed answer. When you use the same key words, you’ll always get the same answer.
However, a generative AI chatbot will generate a new answer each time, using information from its knowledge base. It should give the same information but may phrase it differently. It may feel more personal and like you’re talking to a human.
How can we use generative AI in health and social care?
With new tools, especially those involving innovative technology, there is always equal parts excitement and cautiousness. In this section, we’re going to explore how generative AI can be used in health and social care, along with the benefits it may bring to employees and those in care.
Examples of generative AI in health and social care
We can see generative AI in care in several places already.
A number of health and social care organisations use chatbots on their websites, which can answer a user’s simple question, or direct them towards the next steps. Some organisations are also using generative AI to produce some of their marketing and other written content.
Generative AI has even more significant impact in the wider healthcare field, doing tasks such as enhancing images to aid in diagnosis. Some medical personnel are already using it to write up patient notes – an application that will, no doubt, filter down to social care soon too.
Generative AI in healthcare: what happens next?
As generative AI improves, there are a variety of ways it could help in health and social care, including producing written content. Whether you’re writing letters, marketing material, care plans, or notes after a care call, generative AI may be able to help and speed up the process.
Generative AI could even be used to support people who are isolated. While it would never be a full substitute for social contact, the fact that generative AI can hold a “conversation” could be useful in certain circumstances.
In the wider healthcare field, generative AI could even be used for researching and developing new medication. Some estimates suggest that nearly a third of drugs could be developed by AI within the next few years. This has the potential to revolutionise the care landscape, supporting people to live well for longer.
The benefits of generative AI technology in healthcare
Now we’ve heard about what generative AI is, what about the benefits? There’s many reasons why people are excited about the use of AI in healthcare.
Freeing up staff time
As we all know, health and social care staff are always busy. There aren’t enough hours in a shift to do everything that’s needed (but we do it anyway!).
As health and social care professionals, we work fast. But AI in care can work faster.
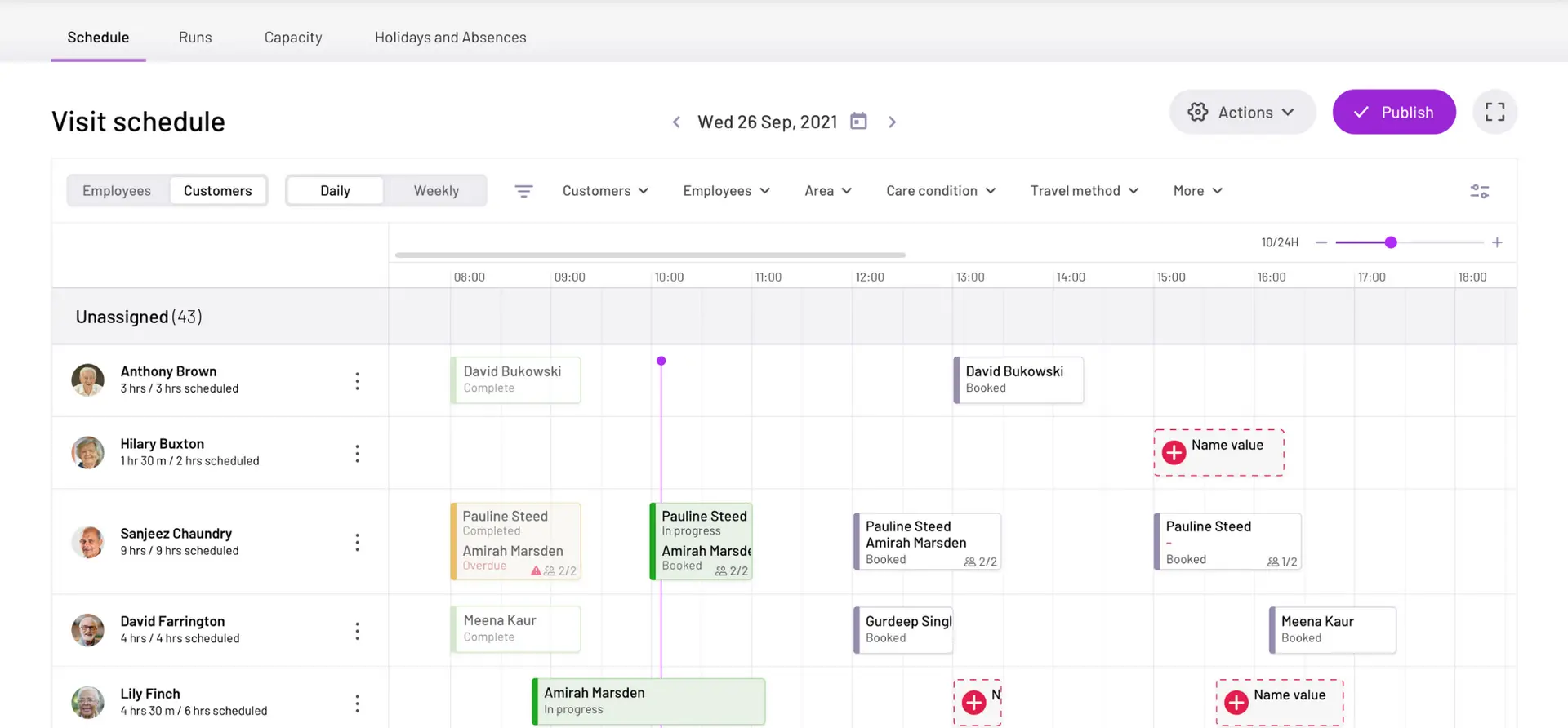
Many organisations are already seeing the benefits of features such as our smart scheduling assistant, part of our care management software.
This can match up carers and service users, based on their preferences and availability. It saves care coordinators some of the tricky work of scheduling, and ensures that clients receive person-centred care with their interests in mind.
Going forward, generative AI will be able to produce additional content quickly, and, in some cases, free up staff time entirely.
Ensuring content is digitised
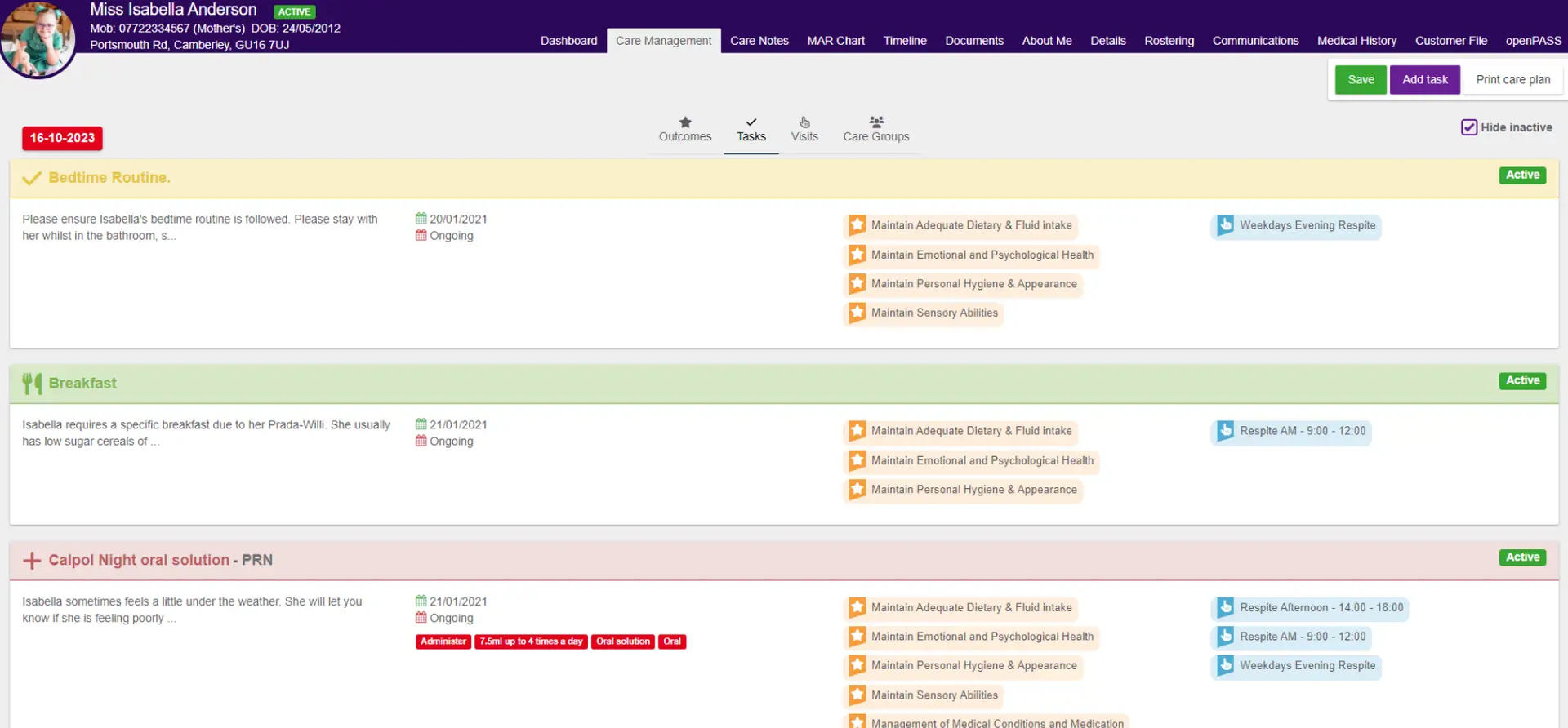
By its very nature, any record-keeping that uses generative AI will be digital.
Digital social care records are increasingly popular – most health and social care organisations have now replaced their paper records with a digital alternative, or are in the process of doing so.
There’s a whole variety of benefits to digital record-keeping, including:
- Increased efficiency, giving staff members more time to spend providing care rather than doing paperwork
- Improved security, along with a lower risk of losing paper records
- Increased accessibility for staff, service users, and family members
- Improved accountability, as accurate records are kept in real time.
Reducing costs
Everyone working in health and social care knows how strained budgets are. If we can work more efficiently and save money, it’s a huge win for the whole team. Going hand-in-hand with freeing up staff time and producing work more quickly, the use of AI in healthcare has the potential to reduce costs.
Improving health outcomes
As generative AI learns from the data it’s been given, it can notice patterns and change its output as it learns – this is known as machine learning. Machine learning in healthcare could lead to improved outcomes for service users, as generative AI systems learn from situations as they happen.
Reducing the risk of human error
As generative AI improves, it has the potential to be able to produce incredibly accurate work. We’ve already seen the benefits of AI’s accuracy in areas such as surgery, where surgical robots can support human surgeons with particularly intricate operations.
While most generative AI solutions aren’t there yet, there might come a time in the future when we’re able to trust them more than the human equivalents.
Cutting-edge innovation
Generative AI in healthcare has the potential to lead to all kinds of new innovations. From the discovery and development of new medication to providing remote care, there may be applications of AI that completely change the landscape of health and social care.
Concerns about the use of generative AI in healthcare
As with all new technology, some people have concerns about how generative AI in healthcare could be used.
Losing the personal touch
Health and social care is a highly sensitive and personal field. People understandably have a strong reaction to hearing that some tasks may be outsourced to a computer.
This reaction tends to be stronger when the task is something that feels more personal – for example, holding a conversation or writing a person-centred care plan.
Service users and their families may worry that organisations will use AI for patient care, causing them to lose out on companionship and crucial social contact.
To an extent, we can mitigate this by consulting with service users and staff members about their comfort levels with AI. In addition, it’s important that there is always human oversight and a trained professional to talk to when necessary – especially when it comes to written content or sensitive issues.

Some jobs could be replaced by AI
Many of the tasks that could be done by AI are handled by human staff members at the moment – they often aren’t new tasks, but current tasks being automated. Staff teams may be worried that this could lead to downsizing.
Potential privacy risks
Some service users or their families may be concerned about privacy risks when using AI. The AI system may need access to the service user’s personal data. If this is stored online, some people may be concerned about potential data breaches.
You may be able to mitigate these concerns by explaining how the AI system will benefit their care, as well as ensuring that you have robust GDPR and data protection policies in place.
Service users’ data may be used to help with machine learning in healthcare, where AI systems are taught to become more accurate based on large data sets. In these situations, privacy risks can be mitigated by only including the necessary data.
Inaccuracies and mistakes
Generative AI is still a new science. Because of that, generative AI models are still learning. Everyone has seen examples of strange things that AI models have produced – there are whole websites dedicated to .
However, as AI continues to learn from data, these inaccuracies will reduce. In time, generative AI output may be indistinguishable from human content – or even better.
Data bias among different communities
We know that there can be differences in people’s symptoms and outcomes, depending on certain characteristics, including age, ethnicity, sex, and co-morbid conditions.
As AI systems are trained on existing data, these disparities will also be reflected in the information fed to them. They could inadvertently perpetuate these disparities in future, leading to some service users receiving unequal treatment and continued poorer outcomes.
If the training data is prepared effectively, with areas of unnecessary bias identified and removed, this should no longer be an issue.
Needing expert oversight
Smaller organisations, or companies incorporating generative AI for the first time, may not have any experts on staff just yet. This isn’t an insurmountable obstacle, but it might require staff training or hiring experts in this new field.
What are your thoughts on generative AI in healthcare?
Now that we’ve explained some of the benefits of AI in healthcare, as well as the concerns, it’s up to you to make the decision: will AI help, or hinder, your care service?
Of course, there’s no pressure to make a decision about generative AI in healthcare right now. The technology is constantly improving, and its applications today may not indicate what is possible in the future.
For now, generative AI technology in healthcare has many benefits, but there are also some valid concerns.




